Humans coexist with birds in the environment and these creatures also dwell near human habitation. Now we ask, what diseases do birds carry to humans? Well, there are plenty of them.
For your information, there are many infections, parasites, and diseases that birds carry to humans. In fact, there are over 60 diseases worldwide that are known to be bird diseases in humans. Those can range from a minor infection to a severe illness and are transmitted once in contact with an infected bird, droppings, or secretions.
In light of this, let’s go over what you should know about those diseases.
Table of Contents
List of Diseases That Birds Carry
1. Fungal infection from birds
Bird fungal infections in humans include histoplasmosis and cryptococcosis.
01 HistoplasmosisIt is caused by the fungus Histoplasma, which lives in the soil where bird droppings have accumulated.
You see, tiny spores of this fungus can mix in the air, leading to infection when inhaled by humans.
However, this is not a worry for healthy individuals as it may go away without special treatment. But, the infection will become severe in people with weak immune systems.
If infected with this diseases caused by birds, the symptoms would be fever, cough, fatigue, chills, chest pain, and body pain,
02 CryptococcosisNext, we have cryptococcosis caused by the fungus Cryptococcus neoformans.
Much like Histoplasma, this disease is also transmitted to humans through inhalation of the dust from dried pigeon droppings containing the microscopic fungus.
Once infected, it will affect the respiratory system and spread to the nervous system and lead to complications such as meningitis and other respiratory problems. The possible symptoms are coughing, chest pain, dizziness, blurred vision, and severe headache.
2. Bacterial infection from birds
For bacterial infection, there are psittacosis and campylobacteriosis.
01 PsiherettacosisIt is among the diseases caused by birds that affect the respiratory system. It may cause inflammation leading to pneumonia. This disease is transmitted through inhalation of dust particles from dried droppings or feathers, through a bite, and through beak-to-mouth contact.
This is caused by the bacteria called Chlamydia psittaci. The symptoms to watch out for are fever, chills, headache, muscle aches, and dry cough.
02 CampylobacteriosisThe illness is caused by the bacteria of the genus Campylobacter. This bacteria is present in animals such as wild birds, considered one of the wild bird diseases.
The possible modes of transmission are eating raw or undercooked foods, drinking contaminated water, or having contact with an infected wild bird. The symptoms are severe abdominal pain, diarrhea, and fever.
3. Bird parasites in humans
Parasites also live in birds, and some of them can also infect humans such as feather mites and cryptosporidiosis.
From the name itself, you can guess that feather mites feed on birds and live in their feathers. Though visible, these insects are so tiny and hard to spot unless you look carefully. Bird mites are tiny black insects walking on eight legs, about under 1 mm long.
Without a host, these bird mites will crawl, infest people’s homes, and feed on humans to survive. Although not technically harmful and poses no serious threat, the problem lies in the uncontrollable itchiness caused by their bites.
How does it affect people? If feather mites bite you, the symptoms would be a severe itch, red bumps on the skin, and swelling in the area of the bite.
Another bird parasitic disease is cryptosporidiosis. The parasite Cryptosporidium parvum lives in the digestive tract, particularly the intestines, of many species of animals, including birds.
Waterborne transmission is the main cause of its rapid spread, or when a human ingests water that is contaminated with the droppings of a bird with this parasite.
Once infected, the main manifestation of this disease is diarrhea. Other symptoms include stomach cramps, dehydration, nausea & vomiting, and weight loss.
4. Wild bird diseases
Wild birds are particularly more likely to bring diseases. One of them is the avian flu, also known as avian influenza or bird flu. This highly contagious disease is a viral infection that occurs among wild birds and many other species.
Though rare in humans, it can still occur, and there are known cases of humans with bird flu, alerting people to be cautious in an area where wild birds dwell.
Wild birds transmit diseases to humans through exposure to an infected bird’s saliva, droppings, and secretions/mucus. During an infection, the symptoms are conjunctivitis, sneezing or coughing, runny nose, low fever, and muscle aches.
5. Bird poop disease in humans
Bird droppings or bird poop are arguably the most responsible for the transmission of bird diseases. An example of that would be avian tuberculosis.
This disease is caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium avium, which affects a large number of bird species and humans. Transmission is through the poop or droppings of an infected bird.
Contact with the contaminated droppings will make a human susceptible to the infection. One scary fact about this bacteria is that it can survive up to 4 years in droppings and soil.
Beware of the symptoms of this disease, such as fever, vomiting, diarrhea, dehydration, and headache.
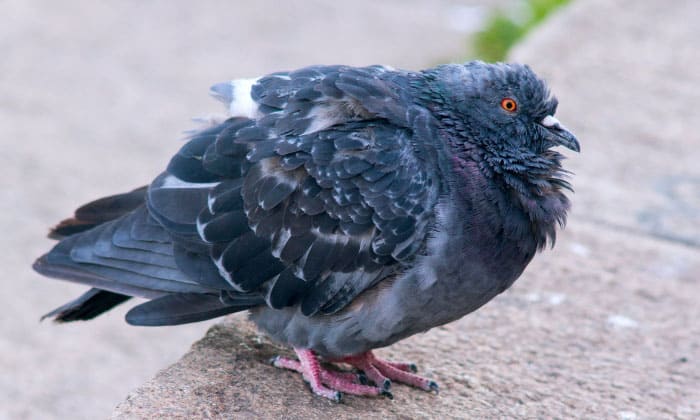
6. Which bird carries the most diseases?
Pigeons are known to be the carrier of most diseases that are known to affect humans. These birds are able to transmit both bacterial and fungal infections to humans through their droppings, secretions, and feathers.
Pigeons have built a reputation for themselves and are being compared to rodents. It is possible that pigeons could bring more diseases than rats solely because of their sanitary habits, according to some bird pest control experts.
Pigeons are often found to be infesting buildings, filling the place with their droppings and leaving behind damaged structures.
The most common diseases caused by pigeon droppings and feathers include cryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, psittacosis, and salmonella.
FAQ
How to prevent contracting diseases from my pet birds?
The most efficient way of preventing diseases from birds is by washing your hands thoroughly before and after handling your birds, their droppings, and any items found in their cage, such as their water dish and feeders.
What to do if I notice any symptoms of diseases from birds?
Immediately seek a healthcare provider, especially for those with weakened immune systems. Most bird diseases, if left untreated, could be potentially fatal.
What other birds carry diseases aside from pigeons?
Other birds known to carry diseases include geese, sparrows, and sterling.
Psittacosis is also one of the parakeet diseases, along with giardiasis, caused by a parasite. Dove diseases are transmitted through dove droppings, feathers, and secretions.
Conclusion
Birds are known to be a carrier of certain diseases and organisms that may threaten our health.
If you are someone who often has close contact with birds or lives in an area with a large population of wild birds, keep in mind the potential risks that come with it and be mindful of the diseases that birds carry to humans.
Practice proper hygiene, and take precautionary measures. Seek medical help immediately if the symptoms of these bird diseases occur.
If there’s anything you would like to add about the diseases birds carry, don’t hesitate to share your thoughts.
Read more: Facts about bird disease in PA

George and I became friends after a birdwatching trip with our new group. And we have been enjoying every adventure together. When he told me the idea of establishing a site that shares our experiences and fun, I immediately agreed. After trials and errors, here we have Thayerbirding.